README.md 19KB
Estructuras de decisión - Juego de desplazamiento de carro
En casi todas las instancias en que queremos resolver un problema hay una o más opciones que dependen de si se cumplen o no ciertas condiciones. Los programas de computadoras se construyen para resolver problemas y, por lo tanto, deben tener una estructura que permita tomar decisiones. En C++ las instrucciones de decisión (o condicionales) se estructuran utilizando if, else, else if o switch. Muchas veces el uso de estas estructuras también envuelve el uso de expresiones de relación y operadores lógicos. En la experiencia de laboratorio de hoy practicarás el uso de algunas estructuras de decisión completando el diseño de una aplicación de juego de colisiones de carros con obstáculos en una pista.
Objetivos:
- Utilizar expresiones relacionales y seleccionar operadores lógicos adecuados para la toma de decisiones.
- Aplicar estructuras de decisión.
Pre-Lab:
Antes de llegar al laboratorio debes:
Haber repasado los siguientes conceptos: a. operadores lógicos b. if, else, else if, switch
Haber estudiado los conceptos e instrucciones para la sesión de laboratorio.
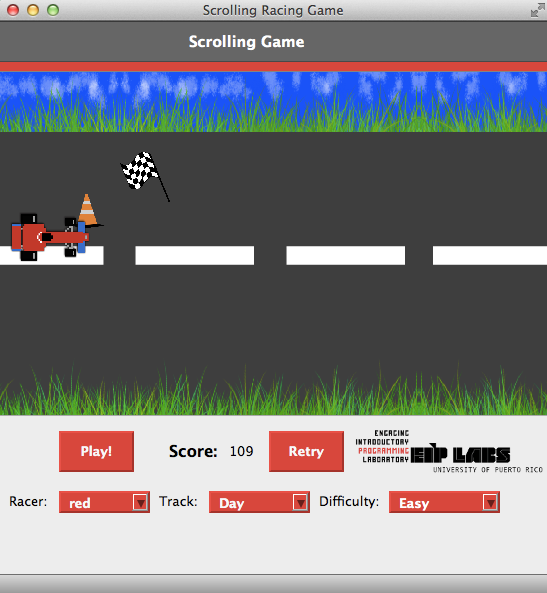
Juego de desplazamiento de carro
Los juegos de colisiones consisten de manejar un objeto esquivando o provocando la posible colisión contra otros objetos. La colisión puede descontar puntos o detener el juego. También hay colisiones con algunos objetos que acumulan puntos. En el juego de esta experiencia de laboratorio el objeto que se maneja es un carrito, los objetos que causan que el juego se detenga son pinos, agujeros, entre otros, y los objetos que suman puntos son las banderas.
Los controles del juego son bien sencillos: la tecla con la flecha hacia arriba desplaza el carro hacia arriba y la tecla con la flecha hacia abajo desplaza el carro hacia abajo. Al jugar, el juego da la sensación de que el carro está en movimiento hacia la derecha usando un método muy simple: desplazando el fondo con sus obsteaculos y banderas hacia la izquierda mientras el carro permanece en el mismo lugar. El jugador puede desplazar el carro hacia arriba o hacia abajo para esquivar los obstáculos y para capturar las banderas. De haber una colisión con un obstáculo el juego se detiene. El jugador puede continuar marcando el botón de Retry.
Sesión de laboratorio:
En esta experiencia de laboratorio practicarás el uso de expresiones matemáticas y estructuras condicionales para implementar la detección de colisiones del carrito contra los obstáculos y contra las banderas.
Tu tarea es completar el diseño de la aplicación del juego.
Ejercicio 1: Familiarizate con las funciones pre-definidas.
El primer paso en esta experiencia de laboratorio es familiarizarte con las funciones (métodos) pre-definidas en el código. Invocarás algunas de estas funciones en el código que completarás para detectar las colisiones.
Instrucciones
Descarga la carpeta
Conditionals-CarScrollingGamedeBitbucketusando un terminal, moviéndote al directorioDocuments/eip, y escribiendo el comandogit clone http://bitbucket.org/eip-uprrp/conditionals-carscrollinggame.Carga a Qt creator el proyecto
CarScrollingGamehaciendo doble “click” en el archivoCarScrollingGame.proque se encuentra en la carpetaDocuments/eip/Conditionals-CarScrollingGamede tu computadora.Configura el proyecto. El proyecto consiste de varios archivos. Solo escribirás código en el archivo
work.cpp. No debes cambiar nada en los demás archivos.Vas a necesitar algunos de los métodos definidos en los siguientes archivos para crear tu código.
car.hycar.cpp: contienen la definición de la claseCar, los métodos de esta clase y sus declaraciones.flag.hyflag.cpp: contienen la definición de la claseFlag, los métodos de esta clase y sus declaraciones.obtstacle.hyobstacle.cpp: contienen la definición de la claseObstacle, los métodos de esta clase y sus declaraciones.play.hyplay.cpp: contienen la definición de la clasePlay, los métodos de esta clase y sus declaraciones.
Familiarízate con los métodos en estos archivos. Pon énfazis en los siguientes métodos:
Car::getYCar(): Devuelve la coordenada en $Y$ de la posición del carro en la pista.Flag::getXFlag(): Devuelve la coordenada en $X$ de la posición de la bandera en la pista.Flag::getYFlag(): Devuelve la coordenada en $Y$ de la posición de la bandera en la pista.Flag::hide(): Esconde la bandera. Desaparece de la pista.Obstacle::getXObstacle(): Devuelve la coordenada en $X$ de la posición del obstáculo en la pista.Obstacle::getYObstacle(): Devuelve la coordenada en $Y$ de la posición del obstáculo en la pista.Play::setScore(n): Recibe un número entero y lo suma a la puntuación del juego.
Nota que no hay método
getXCar()porque el carro no se desplaza en el eje de $X$.
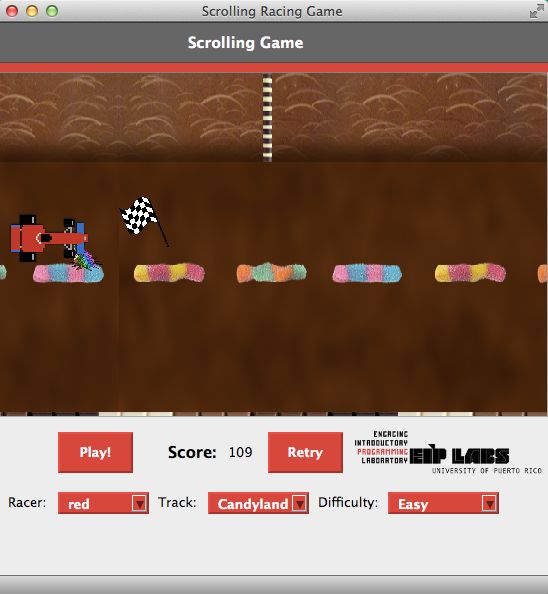
Ejercicio 2: Completar la función para cambiar la pista del juego.
En este ejercicio utilizarás la estructura de condición de C++ switch para cambiar los atributos de la pista. Completarás el método setTrack que se encuentra en el archivo work.cpp. Este método cambia el ambiente de la pista del juego dependiendo del valor que recibe el parámetro track_type.
El método setTrack recibe un valor de tipo Track que puede ser:
* play::DAY - para la pista de día
* play::NIGHT - para la pista de la noche
* play::BEACH - para la pista de la playa
* play::CANDYLAND - para la pista de dulces
Los atributos de la pista que se pueden cambiar son:
* la imagen de la pista usando la función `setTrackPixmap()`
* la imagen de los obstáculos usando la función `setObstaclesPixmap()`
La función setTrackPixmap(Track) ya está definida y recibe una variable de tipo Track que puede ser un valor entre (play::DAY, play::NIGHT, play::BEACH, play::CANDYLAND).
La función setObstaclePixmap(string) ya está definida y recibe una variable de tipo string que puede ser un valor entre (“hole”, “cone”, “it”, “zombie”, “spongebob”, “patric”, “monster”).
Instrucciones
Para completar la función setTrack():
Cambia la imagen de la pista de acuerdo al valor
Trackrecibido.Cambia la imagen de los obstáculos utilizando la estructura de selección
switchde modo que los obstáculos cambien de acuerdo al valor recibido porsetTrack(). Si el tipo de pista que se recibe es:play::DAY- los obstáculos sean de tipo “hole” o “cone”, si elplay::NIGHT- los obstáculos sean de tipo “it” o “zombie”play::BEACH- los obstáculos sean de tipo “spongebob” o “patric”play::CANDYLAND- los obstáculos sean de tipo “monster”
En las opciones que tengan dos posibles obstáculos utilza
rand() % 2para escoger aleatoriamente entre un obstáculo u otro.
Ejercicio 3: Completar la función para colisiones con obstáculos.
En este ejercicio completarás el método obstacleCollision que se encuentra en el archivo work.cpp. La función recibe un objeto de clase Obstacle y otro objeto de clase Car y debe detectar si hay colisión o no entre el carro y el obstáculo. La función devuelve cierto si hay colisión entre el carro y un obstáculo y falso si no hay colisión.
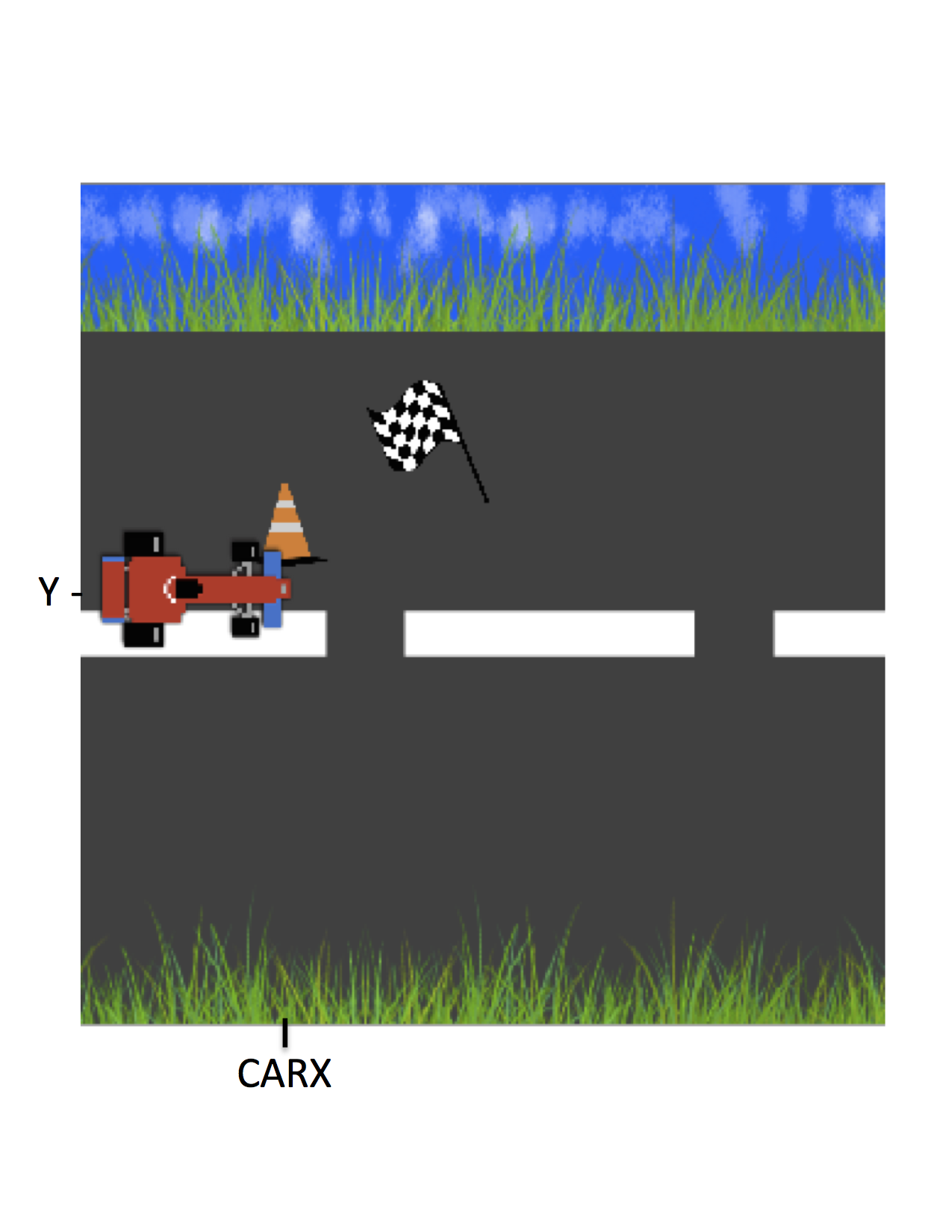
Para detectar la colisión la función debe solicitar las coordenadas del obstáculo y la coordenada en $Y$ del carro. Recuerda que el carro no se desplaza en la coordenada $X$, esa coordenada es fija y está guardada en la variable constante CARX. La colisión ocurre si el obstáculo tiene la misma coordenada en $X$ y está a cierta distancia hacia arriba y abajo de la coordenada en $Y$ como muestra la Figura 1. El rango de distancia del centro del carro hacia arriba y abajo se encuentra guardada en la variable constante OBSTACLERANGE.
Si se detecta una colisión la función debe devolver true y si no debe devolver false.
Figura 1. La imagen muestra las coordenadas $(CARX,Y)$ que debe tener el obstáculo para que ocurra una colisión.
Ejercicio 4: Completar la función para colisiones con banderas.
En este ejercicio completarás el método flagCollision que se encuentra en el archivo work.cpp. La función recibe un objeto de clase Obstacle y otro objeto de clase Flag y debe detectar si hay colisión o no entre el carro y la bandera. Esta función es bien similar a la función del Ejericio 3, excepto que esta función no devuelve valor. Las acciones que ocurren cuando se detecta la colisión se van a tomar dentro de la función.
En este caso si se detecta una colisión, se debe aumentar la puntuación del juego 30 puntos utilizando la función setScore y esconder la bandera utilizando la función flag.hide() para crear la ilusión de que se recogió la bandera en la colisión.
Entregas
Utiliza “Entrega” en Moodle para entregar el archivo work.cpp que contiene el código con las soluciones para escoger la pista y detectar las colisiones. Recuerda utilizar buenas prácticas de programación, incluir el nombre de los programadores y documentar tu programa.
Referencias
[1] Dave Feinberg, http://nifty.stanford.edu/2011/feinberg-generic-scrolling-game/
Selection Structures - Car Scrolling Game
When we want to solve a problem, most of the time there is one or more options that depend on certain conditions being met. Computer programs are written to solve problems, and should therefore have a structure that allows it to make decisions. In C++ the decision (or conditional) instructions are structured using if, else, else if or switch. These structures usually involve the use of relational expressions and logical operations. In today’s laboratory experience you will practice the use of certain decision structures to complete the design of a car and obstacle collision game application.
Objectives:
- Use relational expressions and select appropriate logical operators to make decisions.
- Apply decision structures.
Pre-Lab:
Before arriving at the laboratory you should have:
- Reviewed the following concepts:
a. logical operators
b. if, else, else if, switch
- Studied the concepts and instructions for the laboratory session.
Car Scrolling Game
Collision games consist of maneuvering an object in order to dodge incoming objects to avoid possible collision. The collision can lower the player’s score, or stop the game. Sometimes, colliding with certain objects may increase the player’s score. In the game from today’s laboratory experience, the object the player controls is a car, the objects that cause the game to stop are pines, holes, among others, and the objects that add points to the score are flags.
The controls for this game are simple: the up arrow moves the car up and the down arrow moves the car down. During gameplay, the game simulates the movement of the car towards the right using a simple method: moving the background with its obstacles and flags towards the left while the car stays in the same place. The player can move the car up or down to dodge obstacles and to capture the flags. If the car collides with an obstacle, the game ends. The player can continue by pressing the Retry button.
Laboratory Session:
In this laboratory experience you will practice the use of mathematical expressions and condition structures to implement the car’s collision detection against obstacles and flags.
Your task is to complete the design of the game application.
Exercise 1: Familiarize yourself with the pre-defined functions
The first step in this laboratory experience is to familiarize yourself with the pre-defined functions (methods) in the code. You will invoke some of these functions in the code you will complete to detect the collisions.
Instructions
Download the
Conditionals-CarScrollingGamefolder fromBitbucketusing the terminal, moving to the directoryDocuments/eip, and writing the commandgit clone http://bitbucket.org/eip-uprrp/conditionals-carscrollinggame.Load the Qt project
CarScrollingGameby double clicking theCarScrollingGame.profile found within theDocuments/eip/Conditionals-CarScrollingGamedirectory on your computer.Configure the project. The project consists of various files. You will only write code on the file
work.cpp. You should not change anything on the other files.You are going to need a few methods defined in the following files to create your code.
car.hycar.cpp: contains the definition of the classCar, the methods of the class and their declarations.flag.hyflag.cpp: contains the definition of the classFlag, the methods of the class and their declarations.obtstacle.hyobstacle.cpp: contains the definition of the classObstacle, the methods of the class and their declarations.play.hyplay.cpp: contains the definition of the classPlay, the methods of the class and their declarations.
Familiarize yourself with the methods in these files. Emphasize the following methods:
Car::getYCar(): Returns the $$Y$$ coordinate of the car’s position on the track.Flag::getXFlag(): Returns the $$X$$ coordinate of the flag’s position on the track.Flag::getYFlag(): Returns the $$Y$$ coordinate of the flag’s position on the track.Flag::hide(): Hides the flag.Obstacle::getXObstacle(): Returns the $$X$$ coordinate of the obstacle’s position on the track.Obstacle::getYObstacle(): Returns the $$Y$$ coordinate of the obstacle’s position on the track.Play::setScore(n): Receives an integer number and adds it to the game’s total score.
There isn’t a getXCar() method because the car does not move on the $$X$$ axis.
Exercise 2: Complete the function to change the game’s track.
In this exercise you will use the C++ condition structure called switch to change the attributes of the track. You will complete the setTrack method that can be found in the work.cpp file. This method changes the environment of the track depending on the value of track_type that is given as parameter.
The method setTrack receives a value of type Track that can be:
play::DAY- for a day trackplay::NIGHT- for a night trackplay::BEACH- for a beach trackplay::CANDYLAND- for a candy track
The track’s attributes that can be changed are:
- the image on the track using the function
setTrackPixmap() - the image of the obstacles using the function
setObstaclesPixmap()
The setTrackPixmap() function is already defined and receives a variable of type Track that can be one of the following (play::DAY, play::NIGHT, play::BEACH, play::CANDYLAND).
The setObstaclesPixmap() function is already defined and receives a variable of type string that can be one of the following (“hole”, “cone”, “it”, “zombie”, “spongebob”, “patric”, “monster”).
Instructions
To complete the setTrack() function:
Change the image on the track according to the
Trackvalue received.Change the image of the obstacles using the
switchselection structure such that the obstacles change according to the value received bysetTrack(). If the type of the track that is received is:play::DAY- the obstacles are of type “hole” or “cone”play::NIGHT- the obstacles are of type “it” or “zombie”play::BEACH- the obstacles are of type “spongebob” or “patric”play::CANDYLAND- the obstacles are of type “monster”
With the options that have two possible obstacles use
rand() % 2to randomly select between an obstacle or the other.
Exercise 3: Complete the function for collision with obstacles
In this exercise you will complete the obstacleCollision method that can be found in the work.cpp file. The function receives an object of the Obstacle class and another object of the Car class, and should detect if there is a collision or not between the car and the obstacle. The function returns true if there is a collision between the car and an obstacle and false if there is no collision.
To detect the collision, the function should ask for the coordinates of the obstacle and the car’s $$Y$$ coordinate. Remember that the car does not move on the $$X$$ axis, since that coordinate is fixed and stored in a constant variable called CARX. The collision occurs if the obstacle has the same $$X$$ coordinate, and is a certain distance above and below the car’s $$Y$$ coordinate as shown in Figure 1. The range of the distance of the car’s center upwards and downwards is stored in the variable called OBSTACLERANGE.
If a collision is detected, the function returns true, and if not the function should return false.
Figure 1. The image shows the coordinates $$(CARX,Y)$$ that the obstacle should have for a collision to occur.
Exercise 4: Complete the function for collision with flags
In this exercise you will complete the flagCollision method that can be found in the work.cpp file. The function receives an object of the Obstacle class and another object of the Car class, and should detect if there is a collision or not between the car and the flag. This function is very similiar to the function in Exercise 3, except that the function does not return a value. The actions that occur when a collision is detected are done inside the function.
In this case if a collision is detected, the game’s score should increase by 30 points using the setScore function and hide the flag using the flag.hide() function to create the illusion that the flag was picked up during the collision.
Deliverables
Use “Deliverables” in Moodle to hand in the work.cpp file that contains the function calls and changes you made to the program. Remember to use good programming techniques, include the name of the programmers involved, and document your program.
References
[1] Dave Feinberg, http://nifty.stanford.edu/2011/feinberg-generic-scrolling-game/